What is Additive Manufacturing?
Additive Manufacturing, also known as 3D Printing, is a term used to describe methods that build components directly from CAD or digital models. Because drills, grinders, dies and molds are not used, Additive Manufacturing technologies offer greater design flexibility in the complexity of shapes. So now we can create, for example, seamless interlocking shapes with no assembly required.
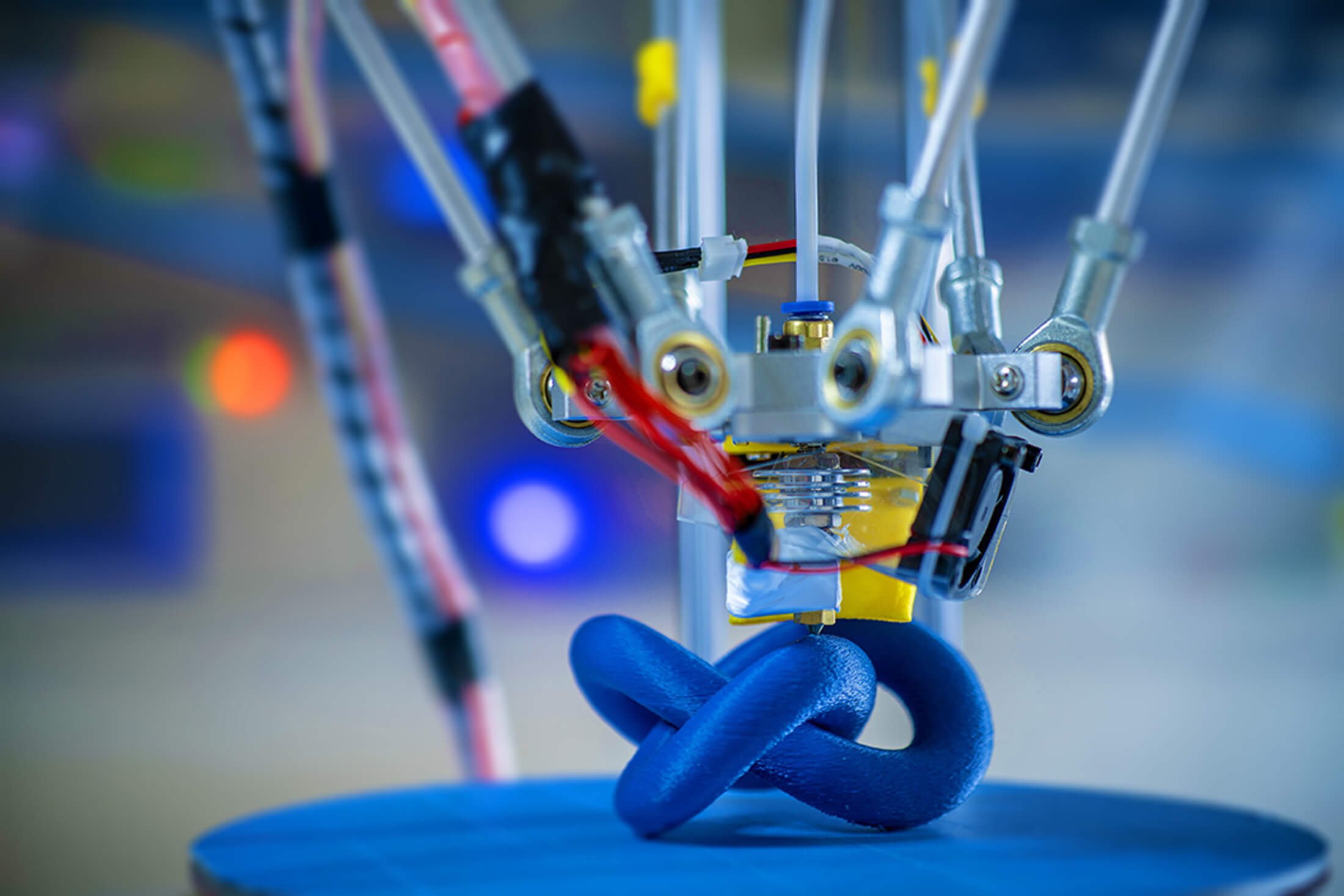
This interlocking shape demonstrates what’s possible with 3D printing. The photo above features a Delta 3D printer in an industrial lab. Image by Science Photo.
Why is Wet Technologies Excited About Additive Manufacturing?
We have yet to fully realize the advantages of Additive Manufacturing. While manufacturers in Aerospace, Automotive, and Medical industries explore rapid prototyping and product development, they may outsource their production runs to third party Additive Manufacturing companies. Wet Technologies works with these companies to perfect the removal of the Additive Manufacturing support structure, and to smooth the surfaces of various materials, including precious metals, titanium, aluminum, alloys, carbon, plastic, polymers and ceramic.
What makes the Wet Tech Process ideal for additive manufacturing post processing?
A Few Different Types of Additive Manufacturing, or 3D Printing, Include:
SLA – Stereolithic
SLA uses UV laser technology to cure sequential layers of photopolymer resin. SLA is popular due to its high resolution and detail, fast build times, and durable substrates.
FDM – Fused Deposition Modeling
FDM “prints” melted thermoplastic materials through a nozzle. The previous layer begins to harden before the next layer is laid down. This method is popular for rapid prototyping. Support structures are often “printed” to stabilize the form as it is built.
PBF – Powder Bed Fusion
PBF uses lasers, electron beams or thermal print heads to melt (or soften) and fuse ultra-fine layers of powdered material. This method can be used to build electrical circuits and well as mechanical parts.
Direct Energy Deposition
A material extrusion process in which a laser or electron beam melts wire, filament or powder. Can be used to repair or add to existing objects.
We welcome comments so please contact us if you’d like to add to the above.








